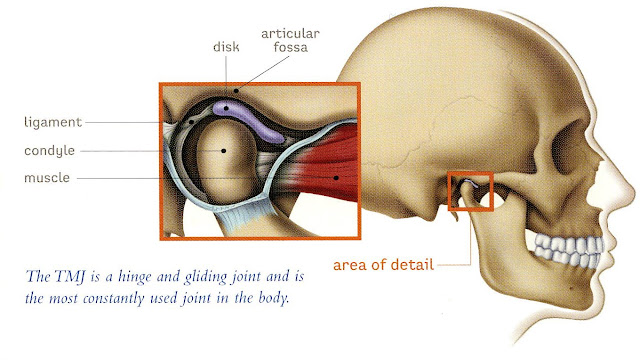
The most complex joints in the body are the two temporomandibular joints (TMJ). These joints are located in front of the ears and connect the lower jaw (mandible) to the temporal bone of the skull. Temporomandibular joints are complex, both rotating and sliding, and involve numerous components: muscles, nerves, tendons, ligaments, bones, connective tissue, and teeth.
TMJ Symptoms are Varied and Mimic Other Health Issues
TMJ is difficult to diagnose because many of the symptoms of TMJ are also symptoms that can be attributed to other heath problems. Some symptoms are periodic; some improve over time while others can worsen. Symptoms of TMJ are described as:- pain in the shoulders or neck
- migraines or chronic headaches
- stiffness of the jaw muscle
- limited movement of the jaw or locking of the jaw
- painful clicking jaw
- popping, or grinding of the jaw when opening or closing the mouth
- ear pain such as pressure or ringing in the ears
- decreased hearing
- dizziness or vision problems
Causes and Treatments for TMJ
Not all causes of TMJ are known but genetic, hormonal, and biological factors can influence the development of TMJ disorder. Factors that can contribute to developing TMJ are teeth clenching or grinding of teeth, nail biting habits, an injury to the area, infections, previous dental treatments, or auto immune disease. Most TMJ patients report a hypersensitivity to pain.TMJ is not recognized as a specialty in either the American Dental Association (ADA) or the American Medical Association (AMA) due to the lack of basic or clinical science; and most insurance companies will not cover treatment for TMJ because there is no standardized method of treatment. There is also no empirical evidence that TMJ can be prevented by any treatment. However, there are some treatments that seem to help diminish TMJ pain.
The National Institute of Health (NIH) suggests the following treatments:
- self-care practices (eating soft food, avoiding extreme movements of the jaw such as yawning, avoiding repetitive movement such as chewing gum, or applying moist heat or cold to the area)
- avoidance of treatments that cause permanent change to the bite or jaw such as crowns, bridges, grinding down of teeth
- avoidance of surgery on the teeth or jaw area
- replacement of the temporomandibular joint as a last resort