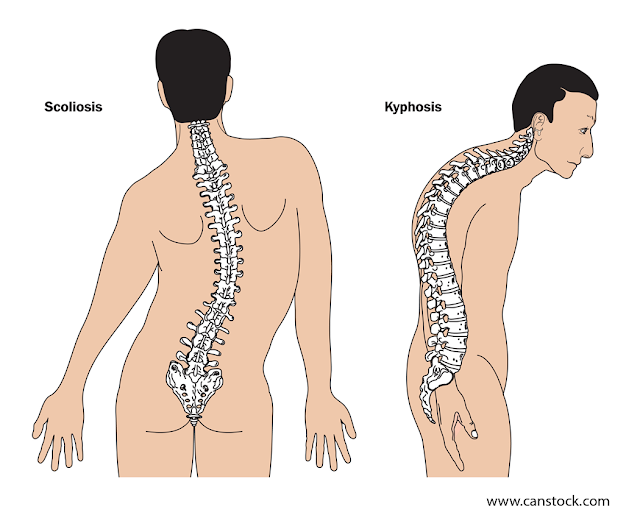
Scoliosis is a condition where the curve of the spine, or backbone, is not aligned correctly. In a person with scoliosis, the spine curves from side to side instead of in a straight line. On an x-ray, the shape of the spine may look like the shape of the letter S or the letter C.
According to the National Scoliosis Foundation in its “Information and Support” section, scoliosis affects two to three percent of the population. An estimated six million people in the United States has some type of scoliosis.
Classifications of Scoliosis
There are five main classifications or types of scoliosis which relate to the possible cause. The most common class is called idiopathic, which means the cause is unknown. This class is further broken down into subclasses which describe the age of onset. Idiopathic scoliosis is sub-classified as infantile, juvenile, adolescent or adult.The second class is called congenital scoliosis. In this class, the abnormality of the spine existed at birth or the cause was due to vertebral abnormalities that were present at birth.
The third class of scoliosis is called neuromuscular. Neuromuscular scoliosis develops as a result of a secondary problem of another medical condition. Conditions such as spina bifida, spinal muscular atrophy, marfan’s disease, cerebral palsy or some kind of physical trauma can impact the formation of the spine as well as the curvature of the spine.
The fourth type is called functional scoliosis. An abnormal curvature of the spine develops because of a problem in another part of the body. One leg being shorter than the other, frequent back spasms or pain in the hips and knees can, over time, impact the normality of the curve of the spine.
The fifth class or type is called degenerative scoliosis. This type is more often seen in adults and is caused by changes in the spine due to age. Some conditions that lead to curvature of the spine due to age include arthritis, weakening of ligaments, muscles, and soft tissue and development of bone spurs.
Signs and Symptoms of Scoliosis
Most cases of scoliosis are mild with slight noticeable changes in the body. Most cases do not cause pain. A person with scoliosis may notice that his clothes do not fit as they did before. Or, he may notice that one pant leg is longer than the other.Other signs of scoliosis may include uneven muscle formation on one side of the spine, a more prominent shoulder blade or rib prominence. The lengths of the hips or the shoulders may be uneven. A female may notice that one breast size or location is slightly different from the other.
In severe cases, scoliosis can cause more severe symptoms. A person may experience slower nerve action or aches and pain, especially in the back. Due to the asymmetry of the chest, a person with scoliosis may find it more difficult to take a deep breath or may have periods of shortness of breath.
In the severest of cases, pressure on the heart and lungs can cause circulatory and more serious breathing problems. And, finally, severe scoliosis can restrict a person’s physical activity and mobility, according to the article “Scoliosis Symptoms” on the Mayo Clinic website.
Treatment for Scoliosis
The treatment or the management of scoliosis is determined by the type of scoliosis, the severity, the person’s age, likelihood of progression and the symptoms. There are four conventional treatments that include observation, physiotherapy, bracing and surgery.Observation involves routine evaluations and x-rays by the physician. Treatment of idiopathic scoliosis will be based on the age when it develops. If the spinal curvature is minimal and remains below a certain degree, no other treatment is needed.
If during the observation period, the spinal curvature progresses, a brace may be recommended. Bracing may be more effective in the juvenile idiopathic type of scoliosis because it is this type that has the greatest tendency to progress. The goal of bracing is to prevent the curvature from getting worse until the adolescent has finished growing. When bracing is not meeting this goal, a more aggressive type of treatment may be indicated.
In the neuromuscular scoliosis types, bones of the spine have developed abnormally and it is this type that most often will require surgery to stop the spinal curvature from getting worse. When the progression of the curvature causes lung and heart problems, surgery may be the only effective treatment.
With functional scoliosis, the type where the abnormality is caused from somewhere else in the body, treatment is not directed on the spinal curvature. Treatment in these cases, if treatment is necessary, is focused on relieving the symptoms and correcting the source of the problem.
A person with degenerative scoliosis or a type of scoliosis that is causing pain, especially in the back, will be treated with pain relieving methods. Some treatments that could be recommended here are physical therapy, exercises, chiropractic intervention, bracing and pain relieving medications. If these and other pain relieving measures fail, surgery may be the only solution.